Ever felt like you’re stuck in a never-ending cycle of putting out fires at work? You’re not alone. Whether you’re in manufacturing, healthcare, or tech, recurring problems can drive anyone up the wall. But what if I told you there’s a way to break free from this frustrating loop? Enter Root Cause Analysis (RCA) – your secret weapon for tackling issues head-on and preventing them from popping up again. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of RCA, exploring its ins and outs, and showing you how to become a problem-solving pro.
Table of Contents
The Nitty-Gritty of Root Cause Analysis
Defining Root Cause Analysis: More Than Just Problem-Solving
Root Cause Analysis isn’t just a fancy term to throw around in meetings. It’s a systematic approach to identifying the fundamental reason behind a problem. Think of it as detective work for your business – you’re not just looking at the crime scene (the symptoms), but you’re digging deeper to find out why the crime happened in the first place.
RCA is about asking “why” until you get to the heart of the issue. It’s like peeling an onion – each layer you remove brings you closer to the center. The goal? To find the root cause that, if addressed, would prevent the problem from recurring.
Why RCA Matters: Real-World Examples That’ll Make You Go “Aha!”
You might be thinking, “Sounds great, but does it really make a difference?” Let me hit you with some real-world examples that’ll show you just how powerful RCA can be:
- The $125 Million Mars Climate Orbiter Mishap: In 1999, NASA lost a $125 million Mars orbiter because one engineering team used metric units while another used English units. A proper RCA could have uncovered this communication breakdown early on, saving millions and preventing a major setback in space exploration.
- Toyota’s Sticky Pedal Fiasco: In 2009-2011, Toyota recalled millions of vehicles due to sudden unintended acceleration. Initial theories blamed floor mats and sticky pedals, but RCA revealed a software glitch in the electronic throttle control system. This discovery led to more effective fixes and improved safety protocols across the automotive industry.
- The Miracle on the Hudson: When Captain Sully Sullenberger landed a plane on the Hudson River in 2009, it wasn’t just luck. The successful outcome was due to years of RCA in aviation safety, leading to improved pilot training, aircraft design, and emergency procedures.
These examples show that RCA isn’t just about fixing problems – it’s about preventing disasters, saving money, and even saving lives. It’s a powerful tool that can transform how organizations operate, leading to improved efficiency, safety, and customer satisfaction.
Camlock Fitting Woes? Your Ultimate Troubleshooting Guide for Industrial Fluid Transfer
The RCA Process: Rolling Up Your Sleeves and Getting to Work

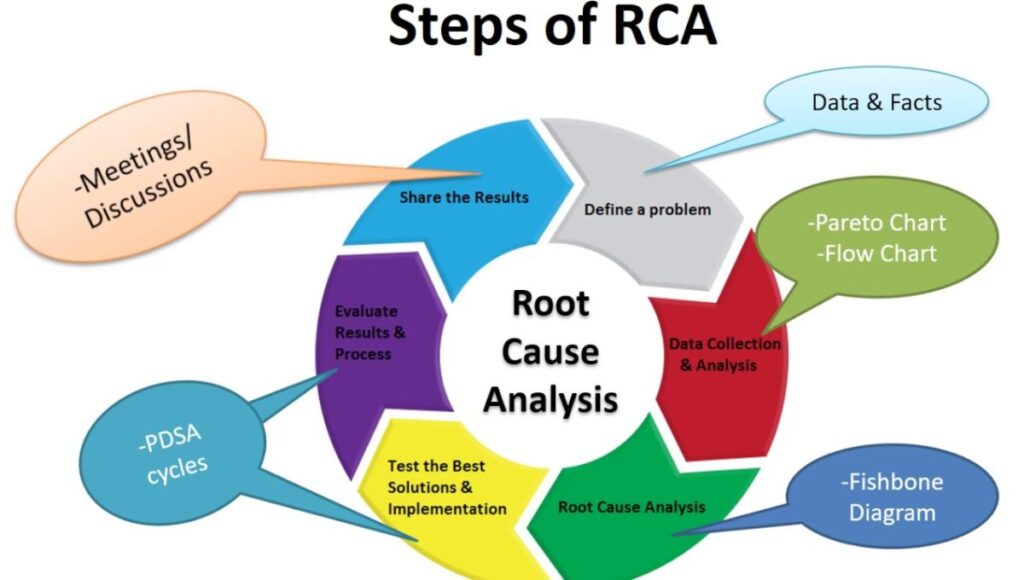
Now that we’ve seen why RCA is so crucial, let’s break down the process step by step. Grab your metaphorical magnifying glass – it’s time to become a problem-solving detective!
Step 1: Houston, We Have a Problem (Identifying the Issue)
The first step in any RCA is clearly defining the problem. This might seem obvious, but you’d be surprised how often people jump to solutions without really understanding what’s going on. Here’s how to nail this step:
- Be specific: Instead of saying “productivity is down,” try “Assembly line B’s output has decreased by 15% over the past month.”
- Use data: Quantify the problem whenever possible. Numbers don’t lie!
- Consider impact: How is this problem affecting your business, customers, or employees?
“A problem well stated is a problem half-solved.” – Charles Kettering
Step 2: Gather Intel Like a Pro Detective
Once you’ve identified the problem, it’s time to collect data. This is where you put on your detective hat and look for clues. Here’s what you need to do:
- Cast a wide net: Gather information from multiple sources – production logs, employee interviews, customer complaints, etc.
- Be objective: Stick to the facts and avoid jumping to conclusions.
- Create a timeline: When did the problem start? Were there any changes or events around that time?
Pro tip: Use a data collection checklist to ensure you’re not missing any crucial information.
Step 3: Hunting Down Possible Culprits
Now that you’ve got your data, it’s time to brainstorm potential causes. This is where creativity meets analysis. Here are some techniques to help you identify possible root causes:
- Brainstorming: Get your team together and let the ideas flow. No idea is too wild at this stage!
- Fishbone Diagram: Also known as the Ishikawa diagram, this visual tool helps you categorize potential causes.
- 5 Whys Technique: Keep asking “why” to dig deeper into each potential cause.
Remember, the goal here is to generate a comprehensive list of possibilities. You’ll narrow it down in the next step.
Step 4: Eureka! Pinpointing the Root Cause
This is where the rubber meets the road. You’ve got your list of potential causes – now it’s time to find the real culprit. Here’s how to do it:
- Analyze the data: Look for patterns and correlations in the information you’ve gathered.
- Test your hypotheses: If possible, run experiments to verify your theories.
- Use logic and critical thinking: Sometimes, the root cause isn’t obvious. You might need to connect the dots in unexpected ways.
Case Study: The Mysterious Machine Breakdown A manufacturing plant was experiencing frequent breakdowns of a critical machine. Initial theories blamed old parts or operator error. However, after thorough RCA, they discovered that recent cost-cutting measures had led to a change in the lubricant used. This new lubricant, while cheaper, wasn’t suitable for the machine’s high-speed operations. By switching back to the original lubricant, breakdowns decreased by 80%, saving the company millions in downtime and repairs.
Step 5: Time to Fix This Mess (Implementing Solutions)
You’ve found the root cause – give yourself a pat on the back! But the job’s not done yet. Now it’s time to implement solutions that will prevent the problem from recurring. Here’s what to keep in mind:
- Address the root cause, not just symptoms: Temporary fixes won’t cut it.
- Consider multiple solutions: There might be more than one way to solve the problem.
- Involve stakeholders: Get buy-in from everyone affected by the changes.
- Create an action plan: Who’s doing what, and by when?
Step 6: Did We Nail It? (Verifying Effectiveness)
Last but not least, you need to make sure your solution actually worked. Here’s how to verify effectiveness:
- Monitor key metrics: Keep an eye on the indicators that alerted you to the problem in the first place.
- Gather feedback: Talk to employees and customers to see if they’ve noticed improvements.
- Be patient: Some solutions take time to show results. Don’t jump to conclusions too quickly.
RCA Tools: Your Problem-Solving Swiss Army Knife

Now that we’ve walked through the RCA process, let’s take a closer look at some of the tools you can use to supercharge your analysis. Think of these as the high-tech gadgets in your problem-solving toolkit.
The Fishbone Diagram: Not Your Average Fish Tale
The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram, is a visual tool that helps you categorize potential causes of a problem. Here’s how it works:
- Draw a horizontal line with the problem statement at the “head” of the fish.
- Add diagonal lines branching off from the main line, representing major categories of potential causes (e.g., People, Process, Equipment, Environment).
- Add smaller “bones” to each category, listing specific potential causes.
Pro tip: Use the 6M’s (Man, Machine, Method, Material, Measurement, Mother Nature) as your main categories for manufacturing-related problems.
5 Whys Technique: Channeling Your Inner Toddler
Remember when you were a kid and kept asking “why” about everything? Turns out, that’s a great technique for RCA! The 5 Whys method involves asking “why” repeatedly to dig deeper into a problem. Here’s an example:
Problem: The production line stopped.
- Why? The machine overheated.
- Why? The coolant level was low.
- Why? The coolant wasn’t refilled on schedule.
- Why? The maintenance checklist didn’t include coolant checks.
- Why? The checklist hasn’t been updated since the new machine was installed.
Root Cause: Outdated maintenance procedures.
Fault Tree Analysis: It’s Not About Blaming Trees
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a top-down approach that visually represents the logical relationship between a failure and its potential causes. It’s particularly useful for complex systems or when dealing with multiple factors. Here’s how it works:
- Start with the undesired event at the top.
- Branch down to intermediate events that could cause it.
- Continue branching until you reach basic events that can’t be broken down further.
- Use logic gates (AND, OR) to show how events combine to cause the top event.
FTA is great for identifying multiple root causes and understanding how different factors interact.
FMEA: Predicting the Future (Sort Of)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a proactive tool used to identify potential failures before they occur. It’s like having a crystal ball for your processes. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- List potential failure modes for a process or product.
- Identify the effects of each failure.
- Determine the severity, occurrence, and detection ratings for each failure mode.
- Calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN) by multiplying these ratings.
- Prioritize actions based on the highest RPNs.
FMEA is particularly useful in product design and process improvement, helping you catch potential issues before they become real problems.
Overcoming RCA Hurdles: When the Going Gets Tough

Root Cause Analysis isn’t always a smooth ride. You might hit some bumps along the way, but don’t worry – we’ve got your back. Here are some common challenges and how to tackle them:
Time Crunch: RCA Ain’t No Speed Dating
One of the biggest hurdles in RCA is time pressure. When a problem is causing major disruptions, there’s often a push to find a quick fix. But remember, the goal of RCA is to find a lasting solution, not just a band-aid. Here’s how to balance urgency with thoroughness:
- Implement temporary fixes: If needed, put a short-term solution in place to mitigate immediate impacts.
- Set realistic timelines: Be clear about how long a proper RCA might take.
- Show progress: Keep stakeholders updated on your findings to demonstrate the value of the process.
Data Overload: Drowning in Information? Here’s Your Life Vest
In today’s data-driven world, you might find yourself swimming in a sea of information. Here’s how to stay afloat:
- Focus on relevance: Not all data is created equal. Prioritize information that’s directly related to your problem.
- Use visualization tools: Graphs, charts, and diagrams can help make sense of large datasets.
- Leverage technology: Consider using RCA software to help organize and analyze your data.
The Blame Game: How to Avoid Pointing Fingers
RCA isn’t about finding someone to blame – it’s about finding solutions. But sometimes, people get defensive when problems are being investigated. Here’s how to keep things constructive:
- Focus on processes, not people: Look at how systems and procedures might have contributed to the problem.
- Encourage open communication: Create a safe environment where people feel comfortable sharing information.
- Lead by example: Admit your own mistakes and focus on learning from them.
RCA Best Practices: Becoming a Root Cause Analysis Rockstar
Want to take your RCA skills to the next level? Here are some best practices that’ll have you solving problems like a pro:
Building Your RCA Dream Team
RCA isn’t a solo sport. Assembling the right team can make all the difference. Here’s what to consider:
- Diverse perspectives: Include people from different departments and levels of the organization.
- Subject matter experts: Bring in specialists who understand the technical aspects of the problem.
- Fresh eyes: Sometimes, someone unfamiliar with the process can spot things others miss.
Creating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
RCA shouldn’t be a one-off event. To really reap the benefits, you need to make it part of your organizational culture. Here’s how:
- Train employees: Offer RCA training to staff at all levels.
- Celebrate successes: Share RCA wins to demonstrate its value.
- Learn from near-misses: Don’t wait for problems to occur – use RCA to investigate close calls too.
Leveraging Technology: RCA Tools for the Digital Age
Technology can be a game-changer in RCA. Here are some tools to consider:
- RCA software: Programs like Taproot® and Causelink® can help streamline the RCA process.
- Data analytics platforms: Tools like Tableau or Power BI can help you make sense of complex data.
- Collaboration tools: Use platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams to keep your RCA team connected.
The Future of Root Cause Analysis: Crystal Ball Not Included
As we wrap up our deep dive into Root Cause Analysis, let’s take a quick peek into the future. While we can’t predict everything, there are some exciting trends on the horizon:
AI and Machine Learning: The New Kids on the RCA Block
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are set to revolutionize RCA. Here’s how:
- Pattern recognition: AI can analyze vast amounts of data to spot trends humans might miss.
- Predictive analytics: ML algorithms can help predict potential problems before they occur.
- Natural Language Processing: AI can analyze text data from reports and interviews to identify potential causes.
Predictive RCA: Solving Problems Before They Happen
The future of RCA is all about prevention. By combining historical data, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics, organizations will be able to identify and address potential issues before they become full-blown problems.
Wrapping It Up: Your RCA Action Plan
Whew! We’ve covered a lot of ground in our journey through Root Cause Analysis. Let’s recap the key points and give you a roadmap for implementing RCA in your organization:
- Understand the basics: Root Cause Analysis is about finding the fundamental cause of a problem, not just treating symptoms.
- Follow the process: Define the problem, gather data, identify possible causes, determine the root cause, implement solutions, and verify effectiveness.
- Use the right tools: Fishbone diagrams, 5 Whys, Fault Tree Analysis, and FMEA are all powerful tools in your RCA toolkit.
- Overcome challenges: Be prepared to deal with time pressure, data overload, and potential blame games.
- Build a culture of RCA: Train your team, celebrate successes, and make RCA a part of your organization’s DNA.
- Look to the future: Keep an eye on emerging technologies like AI and ML that can enhance your RCA capabilities.
Becoming an RCA pro takes practice. Start small, be patient with yourself and your team, and keep refining your approach. Before you know it, you’ll be tackling problems like a seasoned detective, getting to the root of issues and implementing lasting solutions.
So, are you ready to become a Root Cause Analysis rockstar? Your journey to more effective problem-solving starts now. Go forth and conquer those pesky problems – your future self (and your organization) will thank you!
CONCLUSION
Ready to become a problem-solving superstar? Root Cause Analysis is your ticket to breaking the cycle of recurring issues. We’ve covered the basics, from defining RCA to mastering tools like the Fishbone Diagram and 5 Whys. Remember, it’s not about quick fixes – it’s about finding and addressing the real cause. Build a diverse team, embrace technology, and create a culture of continuous improvement. As you practice RCA, you’ll get better at tackling challenges head-on. With AI and predictive analytics on the horizon, the future of RCA looks bright. So roll up your sleeves and start digging – your organization’s efficiency and success depend on it!